Cross infection is spread in a clinical setting between the patient and the doctor, the patient and the patient infectious agent, mode of transmission from person to person contact through indirect spread of pollutants and airborne. The main impact of dental work environment by the patient, medical staff, medical dental equipment three mutually together constitute the route of transmission of pathogens. To sum up, cross-oral route of infection occur in the treatment process may produce the following four kinds: Patients infected doctor, who infected patient, the patient or the doctor spread to the water treatment units or gas system of instruments and items, through equipment or water, gas systems infected patients or doctors.
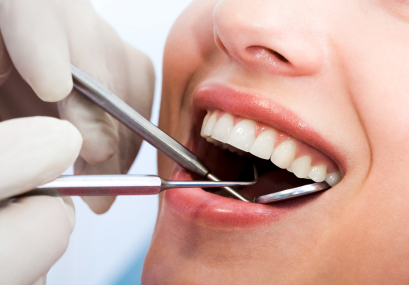
It is the specific issue which caused by the cross infection of dental handpiece and dental turbine during the process of oral treatment. Back in 1963, Black sampled and cultured from clinical dental equipment for dental handpiece and treatment units and found that water treatment units and gas may be polluted by the oral microbial contamination of patients, which is the first report of the possibility of cross-infection via this rout. Ojajarn and other experiments show that at the moment of the comprehensive treatment station stopping gas and turbine handpiece stalling, the head of air is in the state of negative pressure, this can lead the patient's mouth saliva, microorganisms, cutting debris, blood and so on to be sucked back to the inside the dental handpice by the negative pressure, and they can invade into the water treatment units and the gas system through the joints. Microorganisms can settle and form colonies in the handpices’ internal dead place and one microbial membrane layer may be formed on the sidewall of treatment units water pipes and gas system. Typically, the handpiece and the treatment units conduit contaminated water, the surrounding environment and salivary bacteria, pathogenic microorganisms may also exist, such as HIV, HBV, etc. If you use the dental handpiece without sterilization, then the moment when used again for a next patient, the suction substances on rotation with the dental drill with the sprayed mist go into the mouth of the patient causing the cross-infection.